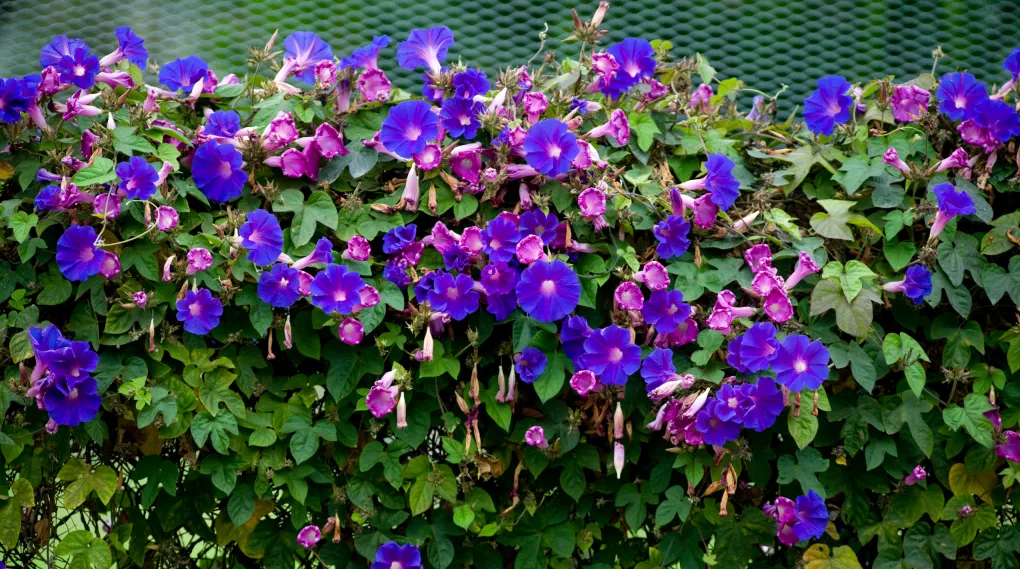
What is Morning Glory?
Morning Glories are climbing vines requiring a vertical support structure to grow. They are appreciated for their vibrant, typically bicolored, trumpet-shaped flowers. Most of them stay true to their name, opening their corollas to honor the morning’s glory and closing them down after sunset, but some do the opposite and bloom only at night.
While they are cultivated purely for ornamental purposes by gardeners and horticulturists worldwide, many Morning Glory species harbor a psychotropic secret — their seeds contain ergine or d-lysergic acid amide (LSA), a natural precursor of LSD.

Morning Glory in Ancient Rituals
The psychoactive and therapeutic effects of Morning Glory seeds were familiar to several ancient civilizations, most notably the Aztecs and the Maya. These cultures used powdered seeds of I. tricolor or I. violacea (tlitliltzin) and I. corymbosa (ololiuqui), respectively, in divinatory and sacrificial ceremonies, as well as in healing rituals, for diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
Tlitliltzin was consumed by Aztec priests (teopixqui) during religious ceremonies. They would drink a cold water infusion of Morning Glory seeds to gain the ability to commune with deities and receive prophetic visions and insights into important future events.
The Maya are known to have brewed a psychoactive drink called xtabentún, a variation of their commonly prepared inebriant mead called balché. Xtabentún would be made by soaking the bark of a local leguminous tree called lancepod in water along with honey from bees fed on I. corymbosa nectar.

The honey would end up containing modest amounts of LSA, and, after fermentation, the intoxicating brew would be consumed communally (often in the form of an enema for maximum effect) to enter visionary or trance states during religious ceremonies.
Ololiuqui was also used by Mayan priests (Ah Kin), who would either consume the seeds on their own or pulverize them and add them to a cacao beverage, potentially along with psilocybin mushrooms (teonanácatl). A preparation of the seeds would also be given in sacrificial rituals to both the victim and their parents in order to induce an altered state of mind before the act.
Morning Glory use was brutally suppressed by the conquistadors as witchcraft, but it remained as an underground practice. The seeds are used to this day in shamanic rituals by a number of indigenous peoples throughout Mexico, including the Chinantec, Zapotec, Mazatec, and Mixtec.
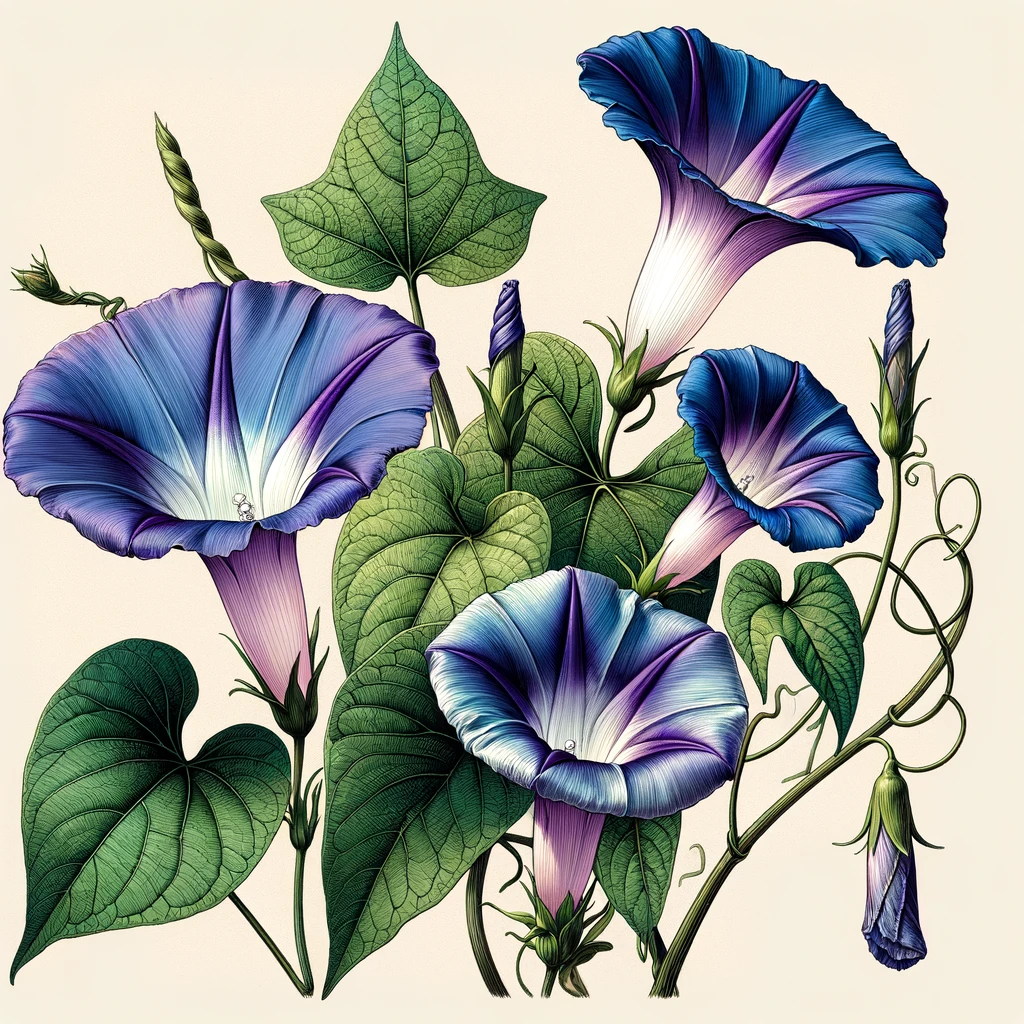

Morning Glory in Traditional Medicine
Aside from its ritualistic uses, Morning Glory was a valued plant in traditional medicine throughout the world.

The Aztecs and the Maya used the seeds as an analgesic and a sedative. They would craft a paste using the seeds and tobacco leaf, which they would then rub on the aching body part; it was especially helpful in cases of gout. Other applications included treating bone fractures, pelvic problems in women, syphilis, flatulence, and even tumors.
Across the Pacific Ocean, in traditional Chinese medicine, Morning Glory was and still is widely used for treating constipation, obesity, phlegm, edema, ascites, hydroncus, lung fever, and ardent fever.
In India, various parts of many Morning Glory species have had a long history of medicinal use primarily for their anti-inflammatory and purgative properties. Morning Glory has also been applied for conditions such as rheumatism, nervous system disorders, bronchitis, fever, dysentery, constipation, dyspepsia, poisonings, skin diseases, scabies, splenopathy, and many others.
Morning Glory Seeds Effects
Although LSA is often rumored to be a ‘weaker form of LSD,’ the reality is that Morning Glory seeds do not induce classic psychedelic effects.

A standard LSA experience is characterized by a sedated, lethargic feeling, with slight perceptual and cognitive alterations, such as enhanced color perception and a boost in mood.
On higher LSA doses, some geometric visualizations and more intense changes in perception of the environment and the self can be observed. This experience is often likened to a waking dream; it may feature both profound inner reflection and a clouded, confused state of consciousness.
Depending on the individual’s metabolism, the initial LSA effects can be felt after 30 minutes to a couple of hours post-ingestion, with the peak of the experience occurring about 2-2.5 hours after the onset. The total duration of the effects is usually about 5-10 hours, although after-effects can linger for up to a day.
Morning Glory seeds can also be microdosed, with many practitioners reporting a range of therapeutic effects from the regimen, including alleviating cluster headaches, relieving pain and relaxing muscles, regulating sleep, suppressing anxiety, and promoting mindfulness and presence.
Microdosing Morning Glory is also a good way to avoid some of the adverse effects that often accompany full-dose experiences.
How Do Morning Glory Seeds Work?
Morning Glory seeds contain several psychoactive alkaloids. The most present one, to which most of the effects are attributed, is the ergoline alkaloid ergine, also known as LSA or d-lysergic acid amide. LSA is a natural precursor to LSD, known for being significantly less potent than its popular chemical relative.
Like LSD, LSA is a serotonergic agonist, with strong affinities for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 serotonin receptors and the α-2 adrenergic receptors, as well as slightly lower affinities for the DA dopamine and α-1 adrenergic receptors.
Although it binds to the same critical receptor (the 5-HT2 serotonin receptor) as classic psychedelics such as psilocybin, mescaline, DMT, and LSD, LSA does so with a much lower affinity, while also missing some biochemical interaction elements present in LSD’s action on this receptor. This is likely the reason behind the lack of intense visionary qualities in the Morning Glory seed experience.
Additionally, Morning Glory seeds contain quite low levels of active compounds. According to an analysis done by Albert Hofmann, I. corymbosa seeds contain 0.012% alkaloids, while those of I. violacea were confirmed in a more recent report to contain 0.06%.
In comparison, Hawaiian Baby Woodrose seeds, whose chemical content overlaps significantly with that of Morning Glory seeds, contain approximately 0.5–0.9% active alkaloids, a reason for many psychonauts to favor them over Morning Glory.
Morning Glory Seeds Side Effects & Precautions
Unlike LSD, the LSA experience is frequently accompanied by side effects. The most commonly reported adverse reactions include:
- A feeling of being intoxicated
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Raised blood pressure
- Muscle tremors
- Drowsiness
- Decreased movement ability
It’s believed that some of these symptoms may be partly caused or exacerbated by toxic chemicals often used to treat the plants during cultivation (perhaps even illegal agents like methylmercury, which are sometimes deliberately applied to prevent human consumption of the seeds).
This is why it’s vital to purchase Morning Glory seeds only from a trusted supplier or to consume them after sprouting and dehusking them (detailed in the next section).
Even when consumed dehusked, however, LSA seems to inherently induce nausea in many people. Ginger tea or anti-nausea medications such as Dramamine can be taken 30-60min before consuming the seeds to counter this reaction.
Barring adverse effects, which are usually mild and self-resolving, LSA is considered a harmless, non-addictive substance with low abuse potential. Tolerance builds up quickly and takes about a week to return to baseline. No withdrawal symptoms have been reported.
Still, as it acts on the serotonergic system, LSA may have a negative biochemical interaction with drugs or substances that also increase serotonin levels. These include MAOIs, SSRIs, and SNRIs — compounds found in common depression medications or plant medicines such as Banisteriopsis caapi (ayahuasca vine) or Syrian rue seeds.
How to Take Morning Glory Seeds
Morning Glory seeds can be consumed in a few ways:
- Crushed or ground into a fine powder, then dissolved in cold water for at least an hour, then filtered and drunk. Adding citrus juice, such as lemon or orange juice, can help mask the flavor.
- Chewed for a few minutes until they become a paste, then either swallowed or kept under the tongue for 30 minutes before being spat out.
- Filed down a bit using a nail file, then soaked overnight in purified or boiled warm water or placed in a moist paper towel for a day or more. Once small yellow sprouts start emerging from the husk, they can be squeezed out from each seed and eaten. This approach might alleviate nausea, but it could also diminish the psychoactive effects (aside from being a logistical hassle when dozens of seeds are involved).

Morning Glory Seeds Legality
Although LSA is a scheduled substance in many countries, Morning Glories are globally popular ornamental plants, and the purchase, possession, and cultivation of their seeds remain legal in most of the world.

Where to Buy Morning Glory Seeds?
Here at Maya Ethnobotanicals, we offer a range of traditional medicinal plants which have been used by indigenous peoples for a variety of purposes since ancient times.
Our products are organically grown, sustainably harvested, and sourced through fair trade, and we sell them with the intention to promote ethnobotanical enthusiasm throughout the world.
We do not advocate for the use of any of our products in illegal ways, nor do we ship any of our botanical samples to countries where they are illegal. We advise our customers to inform themselves thoroughly about their local regulations before placing an order.
If you’re looking for Morning Glory seeds for sale, you may purchase them from our webshop:




